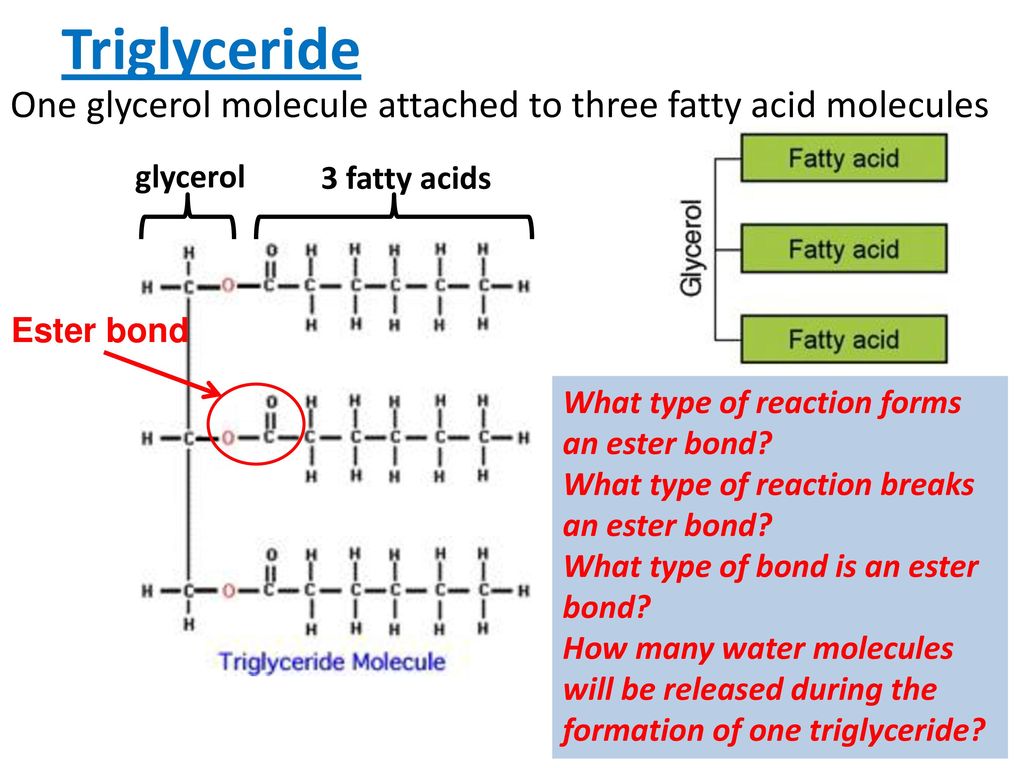
2 A triglyceride is made of one molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids attached to it. A triglyceride is a molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids attached to it.
 What Do These Images Have In Common Ppt Download
What Do These Images Have In Common Ppt Download
They consist of three fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule.
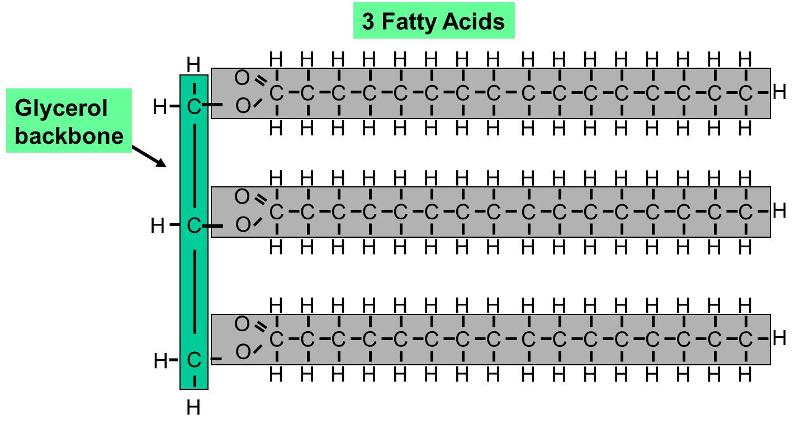
Three fatty acids attached to one glycerol molecule. 3 Fatty acid molecules have long tails made of hydrocarbons carbon chains with hydrogen atoms branching off. Triglycerides consist of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules see Figure 34. A carboxyl acid -COOH group is attached to one end of the chain.
Usually they are dissimilar or two of the three fatty acids. Since fats consist of three fatty acids and a glycerol they are also called triacylglycerols or triglycerides. The major form of lipid in food and in the body.
The most common are the phosphoglycerides which are composed of a glycerol. In the body the majority of the adipose tissue mass is made up of triglycerides. Glycerol is an organic molecule a type of alcohol with.
Similar structures are seen in other triglycerides with various fatty acids esterified to the glycerol molecule. These tails make lipids insoluble in water. Triacylglycerols as the name implies is three fatty acid acyl chains connected to a glycerol molecule by ester bonds Figure 27.
In a fat molecule the fatty acids are attached to each of the three carbons of the glycerol molecule with an ester bond through the oxygen atom. If the number of fatty acids attached to a glycerol happens to be two the ester is called diglyceride or monoglyceride if there is only one molecule of fatty acid attached to a glycerol molecule. The 3 Fatty Acids Attach To This Molecule In A Triglyceride Glycerol Sterol Omega Carbon Glucose.
4 The tails are hydrophobic water-repelling. These are connected to one glycerol molecule via ester linkages Fig. Triacylglycerols also known as triglycerides may have fatty acids of the same simple triacylglycerols or varying types mixed triacylglycerols.
They are called pure fats. Fatty acid molecules have long tails made of hydrocarbons. To break the ester bond and release the fatty acids water is added in a hydrolysis reaction.
By signing up youll get thousands of step-by-step solutions. An example of a triglyceride known as tristearin contains three molecules of stearic acid. Glycerol is an organic compound with three carbons hydrogens and hydroxyl -OH groups.
A glycerol with three fatty acids attached is referred to as a. In fats the three fatty acids are only rarely similar eg tripalmitin tristearin triolein. A lipid consisting of three fatty acids linked to one glycerol molecule.
One molecule of glycerol with three fatty acids attached to it. Organic molecules made up of a chain of carbons linked to hydrogen atoms with an acid group at one end. Each fatty acid joins to the glycerol molecule with a condensation reaction to form an ester bond esterification.
This process happens twice more to form a triglyceride. Types of lipids containing phosphorous. Fatty acids are a long chain of carbons with hydrogens attached to them.
The tails are hydrophobic they repel water molecules. Contain three fatty acid molecules attached to one molecule of glycerol by from CHEMISTRY 171 at De La Salle Health Sciences Institute. Triacylglycerol consists of fatty acids attached to.
This condensation reaction produces a water molecule. During the ester bond formation three molecules are released.
L the Water or Arrhenius Theory. This Module describes the Arrhenius Brønsted-Lowry and Lewis theories of acids and bases and explains the relationships between them.
Modern Theories Of Acids Bases The Arrhenius And
The Arrhenius theory According to Arrhenius theory.

Theories of acids and bases. A base is a substance which ionises in water to give hydroxide ions OH. A base is a proton hydrogen ion acceptor. The Arrhenius Theory of acids and bases.
There are three concepts of acids and bases in current use. It also explains the concept of a conjugate pair - an acid and its conjugate base or a base and its conjugate acid. A pair of species differing by a single proton is called a conjugate acidbase pair.
This we can conclude because it has a lot more specific information that is more developed than that of Arrheniuss. An acid is a proton hydrogen ion donor. Oxygene means acid-forming in Greek and reflects the mistaken belief that the element oxygen was responsible for a compounds acidic properties.
Guidance Students should know the representation of a proton in aqueous solution as both H aq and H 3 O aq. A BrønstedLowry acid is a protonH donor and a BrønstedLowry base is a protonH acceptor. They are Arrhenius Theory.
So which theory Arrhenius or Bronsted-Lowry is the most suitable to the society then. Amphiprotic species can act as both BrønstedLowry acids and bases. Arrhenius Theory The Swedish chemist Svante Arrhenius published his theory of acids and bases in 1887.
Neutralisation happens because hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions react to produce water. According to Lewis theory of acids and bases it states that acids as electron pair acceptors and bases as an electron pair donors. These theories include the Arrhenius theory the Bronsted-Lowry theory and the Lewis theory of acids and bases.
This page just tidies things up. Remember however that the aqueous hydrogen ion is actually chemically bonded to water that is H3O. Acid can remain energetically favorable after a loss of H molecule.
Hydrochloric acid is neutralised by both sodium hydroxide. Limitations of the theory. Acidic substances are usually sour in nature and are primarily a molecule that has the capacity to donate an H ion.
Much more accurate definitions of acids and bases have been created. The theory of acids and bases like many other chemical theories has undergone numerous changes in recent times. Arrhenius Concept of Acids and Bases According to the Arrhenius concept of acids and bases an acid is a substance that when dissolved in water increases the concentration of hydronium ion H3O.
It also explains the concept of a conjugate pair - an acid and its conjugate base or a base and its conjugate acid. The Bronsted-Lowry Theory of acids and bases. If you have worked through the various reactions of acids and bases in this section then you will have met almost all of the reactions you need to know about.
Three concepts are explained this acids bases mechanism. An acid is a substance which ionises in water to give hydrogen ions H. 2 the Proton or Br0nsted-Lowrv Theory.
After made researches we can conclude that Bronsted-Lowrys theory on acids and bases is the most suitable theory to the society. An acid is a substance which dissociates in water to produce one or more hydrogen ions H. Acids are substances which produce hydrogen ions in solution.
Three different theories have been put forth in order to define acids and bases. The Arrhenius theory wouldnt count this as an acid-base reaction despite the fact that it is producing the same product as when the two substances were in solution. An acid is a hydrogen ion.
Acid-base theory has been developed by scientists around the world and its vocabulary has been influenced by their languages. Always the changes have been such as to make the theory more general. What is the Bronsted-Lowry theory.
The three main theories in use today are. THEORIES OF ACIDS AND BASES This page describes the Arrhenius Bronsted-Lowry and Lewis theories of acids and bases and explains the relationships between them. There are three different theories of what acids and bases are but the most useful one at this level is the Bronsted-Lowry theory.
A brief description of each of these theories is provided in this subsection. Acids and bases can be defined via three different theories. Bases are substances which produce hydroxide ions in solution.
Theories of Acids and Bases. It can be simply explained by these two points. Arrhenius Acids and Bases 1.
Strong and Weak Acids. They are based on the structure and composition of acids bases. Theories of acids and bases 8.