American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language Fifth Edition. Naturally acquired active immunity Immunological protection that occurs unintentionally following exposure to an organism such as with infectious disease.
Active immunity is usually permanent.
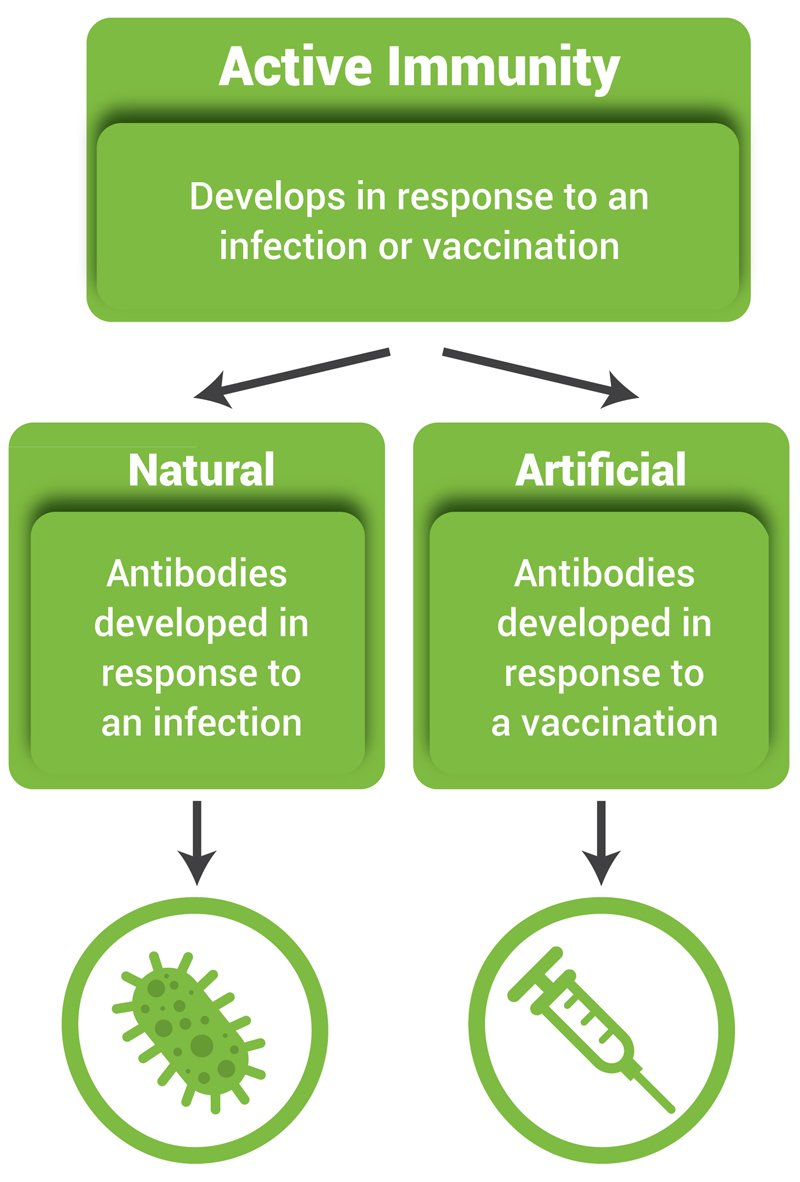
Definition of active immunity. Antibodies are created by the recipient and may be stored permanently. Active immunity can be acquired in two ways by contracting an infectious disease such as chickenpox or by receiving a vaccination such as against chickenpox. Active immunity is usually permanent meaning an individual is protected from the disease for the duration of their lives.
Active Immunity The natural immune response to an antigen by infectious exposure or inoculation resulting in the formation of specific antibodies and protection from subsequent infection by the same pathogen. Active immunity in American English immunity to a disease due to the production of antibodies by the body see also passive immunity Websters New World College Dictionary 4th Edition. The production of antibodies against a specific agent by the immune system.
The situation in which the body produces its own antibodies substances in the blood that. Immunity produced by the body in response to stimulation by a disease-causing organism or other agent. Immunity resulting from the development of antibodies in response to the presence of an antigen as from vaccination or exposure to an infectious disease.
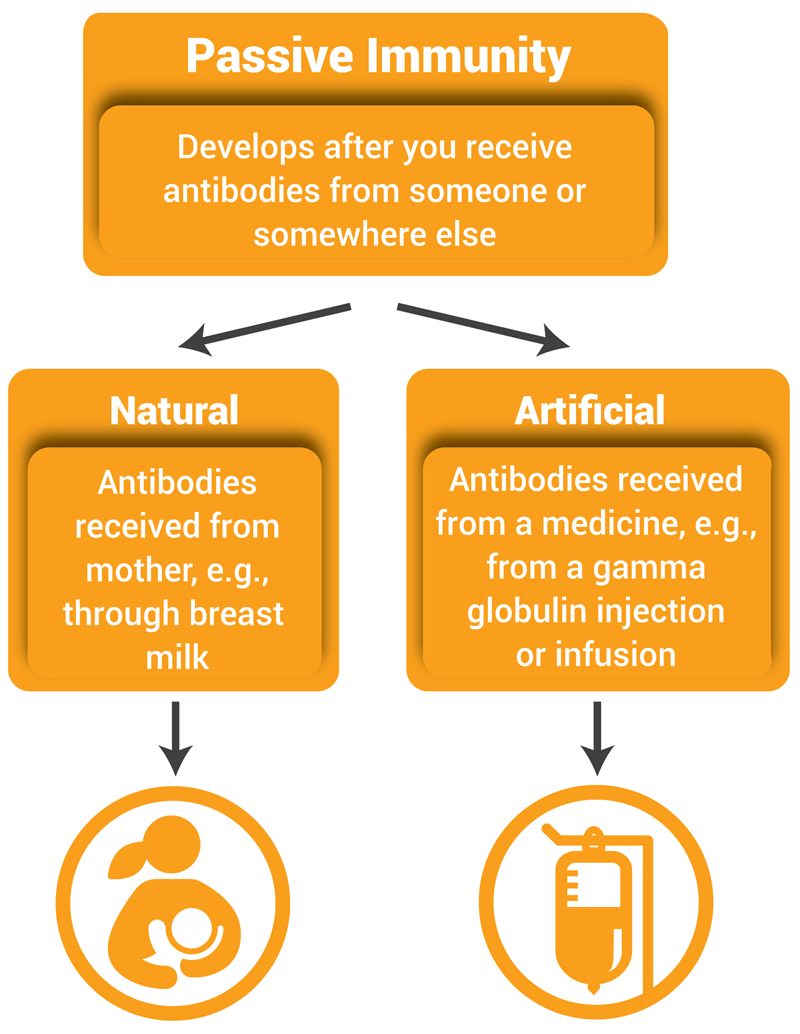
In order for an individual to acquire immunity ones body must be stimulated to produce its own immune response components active immunity or these substances must be produced by other persons or animals and then passed on to the person passive immunity. Immunity that develops after exposure to a disease-causing infectious microorganism or other foreign substance such as following infection or vaccination. The production of antibodies against a specific disease by the immune system.
Active immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease. The situation in which the body produces its own antibodies substances in the blood that. Active immunity definition is - usually long-lasting immunity that is acquired through production of antibodies within the organism in response to the presence of antigens.
Active immunity can be acquired in two ways either by contracting the disease or through vaccination. Active immunization can occur naturally when a microbe or other antigen is received by a person who has not yet come into contact with the microbe and has no pre-made antibodies for defense. Active immunity definition immunity in an organism resulting from its own production of antibody or lymphocytes.
Active immunization is the induction of immunity after exposure to an antigen.
Examples of natural immunity are the lysozyme found in tears saliva and other body secretion acidic pH of the gastrointestinal and vaginal tracts and interferon produced by body cells to protect against viruses. Natural Active Immunity.
 Difference Between Active Immunity And Passive Immunity Explained
Difference Between Active Immunity And Passive Immunity Explained
Wild infection for example with hepatitis A virus HAV and subsequent recovery gives rise to a natural active immune response usually leading to lifelong protection.
Example of natural active immunity. Active immunity is immunity that develops as a result of natural or deliberate exposure to an antigen. Vaccinations stimulate the immune system with an antigen. Immunization of chickenpox hepatitis flu and polio are some examples of active immunity.
Also known as natural resistance. This type of immunity is natural because deliberate exposure does not induce it. To artificially immunize an individual a weakened or killed version of the same antibody is used against which the immunity is sought.
And The IgA and IgG found in human colostrum and milk. An allergic reaction is an extreme response to an antigen resulting from active immunity. In a similar manner administration of two doses of hepatitis A vaccine generates an acquired active immune response leading to long-lasting possibly lifelong protection.
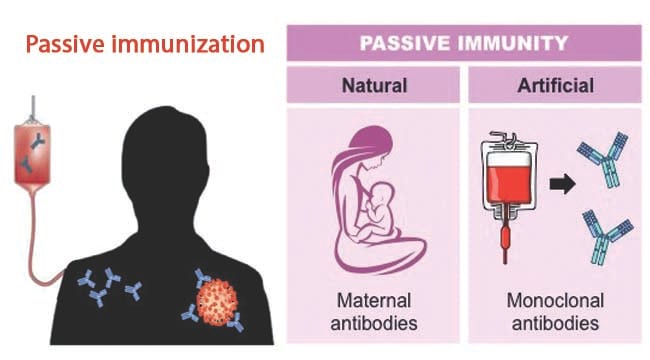
The placental transfer of IgG from mother to fetus during pregnancy that generally lasts 4 to 6 months after birth. Exposure to the disease organism can occur through infection with the actual disease resulting in natural immunity or introduction of a killed or weakened form of the disease organism through vaccination vaccine-induced immunity. The IgA and IgG found in human colostrum and milk of babies who are nursed.
In addition to the IgA and IgG. Naturally acquired active immunity occurs when a person is exposed to a live pathogen and develops a primary immune response which leads to immunological memory. For example a by-product of the enzymatic activity of the complement system acts as a chemotactic factor attracting T lymphocytes and macrophages to the invasion site.
Acquired immunity makes your immune system stronger. In another example although T lymphocytes are not required for the production of antibody there is optimal antibody production after interaction between T and B lymphocytes. Natural immunity is a general and non-specific resistance to infection possessed by all healthy individuals.
The immune system creates its defense against the antibody by the eventual production of antibodies. Natural immunity The ability to resist infection that does not depend on prior experience of the invading organism and the resultant production of antibodies or amendment or selection of LYMPHOCYTES. Active Immunity - antibodies that develop in a persons own immune system after the body is exposed to an antigen through a disease or when you get an immunization ie.
There are two examples of passive naturally acquired immunity. The body responds by making its own antibodies. A baby receiving antibodies from her mothers breast milk and injection of antisera are examples of passive immunity.
This ensures that when the individual comes in natural contact with this antigen later the immune. These antibodies generally last 4 to 6 months. Learn Examples On Natural Acquired Active Immunity Meaning Concepts Formulas Through Study Material Notes Embibe Com Micro Ch16 Preparation Cell Mediated Humoral Response Flashcards Quizlet Give An Example Of Artificially Active Immunity And Artificially Passive Immunity Biology Mineral Nutrition 12602809 Meritnation Com Artificially Acquired Active Immunity Example.
A vaccination is an example of active immunity. Natural active immunity occurs when an individual comes in natural contact with an antibody. Active immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease.
The immune system then produces B and T cells that quicken and strengthen the bodys response to repeated infection. Either way if an immune person comes into contact with that disease in the future their immune. Active naturally acquired immunity refers to the natural exposure to an infectious agent or other antigen by the body.
Vaccines for example expose your immune system to small amounts of pathogens that wont make you sick. The placental transfer of IgG from mother to fetus during pregnancy. Examples of Active Immunity An example of natural activity immunity is fighting off a cold.
An example of artificial active immunity is building up a resistance to a disease due to immunization. The phenomenon of natural immunity can be illustrated equally well with examples from the respiratory intestinal or genital tracts where large surface areas are exposed to potentially infective agents and yet infection does not occur. There are two examples of passive naturally acquired immunity.
Immunity that develops after exposure to a disease-causing infectious microorganism or other foreign substance such as following infection or vaccination. If an organism causes local infection or gains entry into the bloodstream a complicated series of events ensues.