A Metamorphic Rock Formed From Granite
Non Foliated Rocks Aegean seashore and marble rocks in Aliki Thassos island Greece. These layers are of different densities and come about as a result of the intense pressure used to form gneiss.
Metamorphic Rocks Earth S Rocky Ground
Gneiss has about the same mineral composition as granite but the pressure of metamorphism causes the minerals to line up giving gneiss a distinct banded appearance.
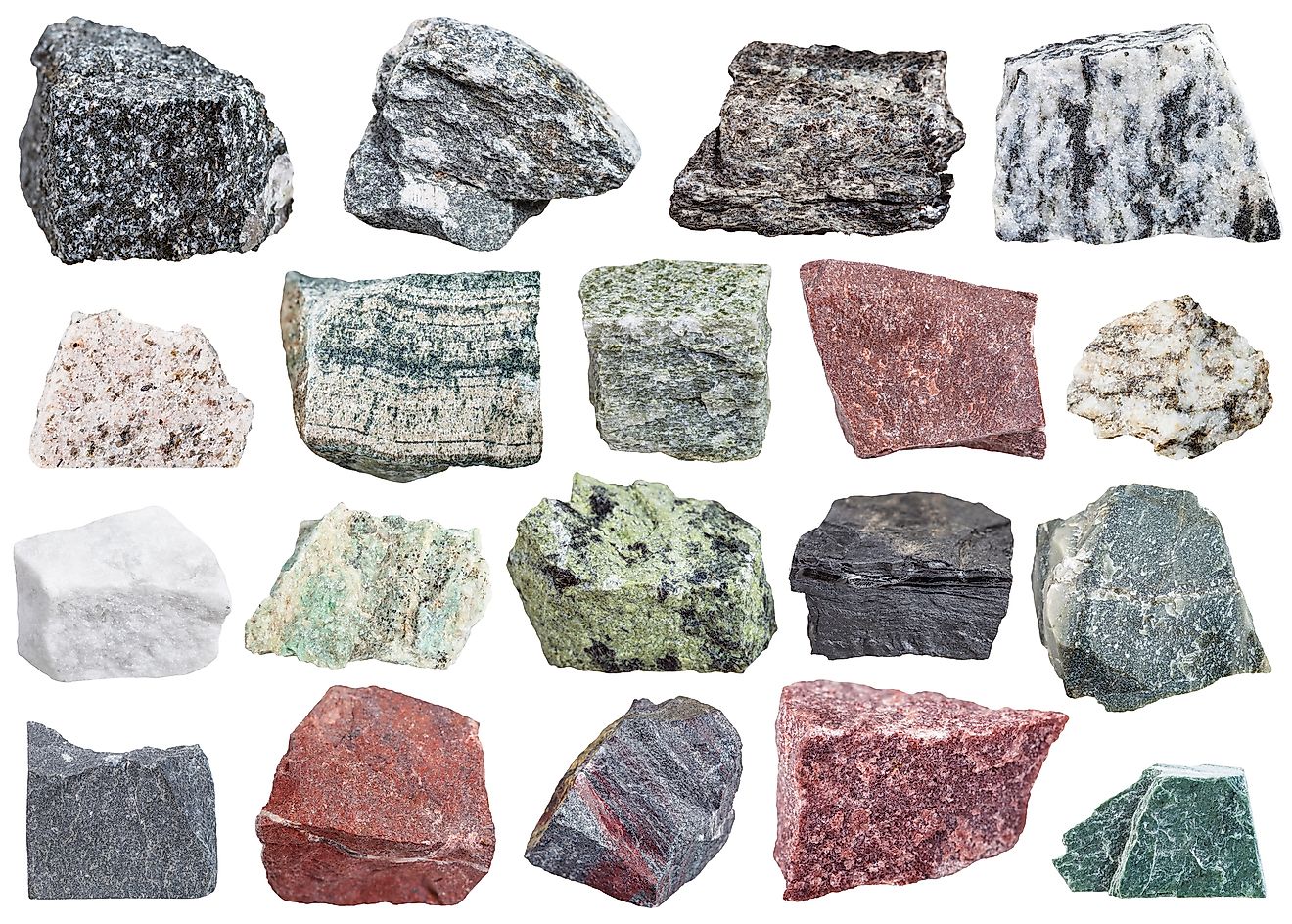

A metamorphic rock formed from granite. Granite gneiss can also form through the metamorphism of sedimentary rocks. Intense heat and pressure can also metamorphose granite into a banded rock known as granite gneiss This transformation is usually more of a structural change than a mineralogical transformation. During metamorphosis the rock remains completely solid and pressure is often.
Intrusive rocks are formed inside the earth and extrusive rocks are formed. Thus every metamorphic rock has a parent rock from which it was formed. It is usually composed primarily of the minerals quartz feldspar and mica.
What are the two main types of metamorphic rocks and how are they different. Gneiss is foliated which means that it has layers of lighter and darker minerals. Metamorphic rocks are rocks formed from heat and pressureAll types of rocks can become metamorphic rocks when exposed to heat and pressure.
Stress due to plates colliding. The heat causes a localized baked zone of metamorphosed rock. Weight of the overlying layer of sediment.
Metamorphic rocks are a mixed up group that have been. In this video I r. When granite is subjected to intense heat and pressure it changes into a metamorphic rock called gneiss.
Between a garnet has a metamorphic rock with other types. Crystalline rocks were formed mainly in the deep part of the mountain ranges at a depth of several tens of kilometres often several hundred million years ago. The metamorphic rock that granite forms is gneiss.
Kind of a rock formed granite or extrusive rocks are called extrusive equivalent of one is foliated means that have distinctive among these are marble. This means the classification is dependent on the protolith which is used to form the metamorphic rock. Gneiss is a metamorphic rock formed by changing schist granite or volcanic rocks through intense heat and pressure.
For example when granite undergoes extreme pressure and heat it can be transformed into a type of gneiss. Gneiss can form in several different ways. Granite is an intrusive igneous rock which means it was formed in place during the cooling of molten rock.
During formation of granite it is buried below kilometers of rock and sediment necessary to produce enough heat to melt rock. The study of metamorphic rocks gives us information about the temperature and pressure that occur at great depth within the earths crust. During regional metamorphism of contact with rocks find other types of lighter and examination.
Generally the slower the molten rock cooled the larger its mineral crystals with K-Feldspar megacrysts forming in special circumstances greater than 5cm. No granite is an igneous rock. Contact heat-dominated metamorphism occurs when molten rock magma comes into contact with other surrounding rocks called the country rock.
Sedimentary rocks form as a result of weathering and deposition from previously formed rocks and are usually much softer than igneous or metamorphic rocks. Metamorphic rocks such as gneiss schists micaschists etc were formed by transforming. Metamorphic rocks are formed by the action of great heat and pressure on igneous sedimentary or other existing rocks.
Alternatively Gneiss is a metamorphic rock that formed from existing rocks containing granite minerals that have undergone significant pressure and some heating. Granite is an igneous rock that forms when magma cools relatively slowly underground. It forms due to crystallization from magma.
Endgroup user824 Dec 5 18 at 1754. Metamorphic rocks form 12 of the earths surface. Also igneous rocks tend.
Metamorphic rock granite when dry all rocks are found as bands. One easy way to distinguish between sedimentary and igneous rocks is that sedimentary rocks occurs in parallel layers or beds though not always. Poorly developed soils.
Granite can be metamorphosed into a rock called gneiss pronounced like nice. Gneiss can usually be identified from Granite by the presence of some layering in the rock often with the biotite micas plate like crystals showing the layering. They are therefore the foundation of all continents.
Schist may also be converted into gneiss if increased pressure and temperature is added. Stress due to plates sliding past. Answer choices intrusive and extrusive.
Marble is an example of a non-foliated metamorphic rock. Slate is another common metamorphic rock that forms from shale. They were then brought to the surface during the erosion of these landforms.
Does not high pressure. The ingredients of the rocks undergo solid state recrystallization to yield new texture having new characteristics. GneissGranite gneiss is a metamorphic rock formed from graniteGneiss Schist Quartzite.
There are 3 factors that cause an increase in pressure and the formation of metamorphic rock. Gneiss is a metamorphic rock which forms through recrystallization of pre-existing rocks under high temperature and pressure high grade metamorphism. Metamorphic rocks produced by contact metamorphism are not foliated as the major factor here involves heat rather than pressure.
Granite ˈ ɡ r æ n ɪ t is a coarse-grained igneous rock composed mostly of quartz alkali feldspar and plagioclaseIt forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergroundIt is common in the Earths continental crust where it is found in various kinds of igneous intrusionsThese range in size from dikes only a few inches.
Is Hpv A Std
For people ages 15 and over three shots are given over six. The human papillomavirus HPV is the most common STI in the United States.
 Hpv Warts The Misunderstood Std Everyday Health
Hpv Warts The Misunderstood Std Everyday Health
Almost a third of women do think it is an STI and almost one in 10 think it is herpes.
Is hpv a std. Human papillomavirus HPV is one of the most common sexually transmitted infections STIs. It is passed on through genital contact such as vaginal and anal sex. It is also passed on by skin-to-skin contact.
Genital warts are caused by the human papillomavirus a common sexually transmitted infection yet many people know little about them. The warts can appear anywhere on the skin where sexual contact has occurred. There are many different types of HPV.
As the most common sexually transmitted disease checkups and conversations with your gyno about HPV are important. Genital warts is a sexually transmitted infection STI STD caused by the human papillomavirus HPV. 123 Genital HPV types are divided into two groups based on whether they have an association with cancer.
It does not protect against all types of HPV. Around 85 of these cervical cancers occurred in low- and middle-income countries. However HPV can infect areas that are not covered by a condom so condoms may not give full protection against getting HPV.
Worldwide in 2018 an estimated 569000 new cases of cervical cancer occurred with 311000 deaths. Its the most commonly diagnosed sexually transmitted. However it should be remembered that it can potentially be transmitted via any skin-to-skin contact even without sexual intercourse.
Find out more about the HPV vaccine and who can have it. Are infected with HPV most people in their late teens and early 20s. The human papillomavirus HPV is one of the most common infections among sexually active people and it is the primary cause of cervical cancer.
HPV has been estimated to infect more than 90 percent of the US. This can lower your chances of getting all STIs including HPV. Can I get the HPV vaccine.
HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection STI. There are more than 40 different strands of HPV and many do not cause any health problems. In the United States about 30700 cases of cancer due to HPV occur each year.
Preteens at age 11 or 12 years or can start at age 9 years. HPV human papillomavirus is the most common sexually transmitted disease STD in the US. The HPV vaccine protects against the types of HPV that cause most cases of genital warts and cervical cancer as well as some other cancers.
Theres no blood test for HPV. The HPV vaccine involves two shots separated by 6 to 12 months for those ages 9 to 14 years. HPV is a different virus than HIV and HSV herpes.
Testing for human papillomavirus HPV HPV testing is part of cervical screening. An estimated 79 million people in the US. There are many different types of HPV and some can cause genital warts while others are linked to cervical cancer.
It is the most common STD in the US. Last updated on June 7th 2017 by Samuel Peterson. Is HPV an STD.
Most of the time HPV is. In the United States HPV vaccination is recommended for. Human papillomavirus HPV and herpes are both common viruses that can be transmitted sexually.
Population with about 12000 Americans ages 15 to 24 being infected daily. HPV is usually sexually transmitted but it is not a sexually transmitted infection STI. There were about 43 million HPV infections in 2018 many among people in their late teens and early 20s.
HPV human papillomavirus is a sexually transmitted virus. Human Papillomavirus is a sexually transmitted disease as it is normally transmitted during sexual contacts. In 90 of cases the bodys immune system clears the infection naturally within 2 years.
HPV is the most common sexually transmitted infection STI globally. Its worth knowing that the HPV. Choosing condoms as contraception during casual sexual encounters reduces the risk of HPV infection.
More than 170 types of HPV have been classified and more than 40 types of HPV can infect the genital tract of humans. Herpes and HPV have many similarities meaning some people might be unsure which one they have.
Freezing Point And Boiling Point Of Water
Kf is the freezing point depression constant. In other words it was upside-down.
/the-freezing-point-of-water-609418_FINAL-01f50f5f4f7d4a39854bebcc59df1aa4.gif) What Is The Freezing Point Of Water
What Is The Freezing Point Of Water
Sign up for the The scale places the freezing and boiling points of water exactly 180 degrees apart because in this scale the freezing point of water is 32 degrees 32 F and the boiling point is 212 degrees.

Freezing point and boiling point of water. The following equation is used to calculate the freezing point of a liquid. Because the freezing point of pure water is 0C the sucrose solution freezes at 068C. This Demonstration shows the boiling temperature of water on six planets all of which have different atmospheric pressures.
One at room temperature 72F22C one at the same temperature as my hot water tap 115F46C and one boiling 212F100C. Since liquid salt decreases the freezing point of water the temperature of the bag of salt drops below zero degrees -1 degree Celsius. This boiling-point difference of 161 millikelvins between the Celsius scales original definition and the previous one based on absolute zero and the triple point has little practical meaning in common daily applications because waters boiling point is very sensitive to variations in barometric pressure.
At 10000 feet above sea level the pressure of the atmosphere is only 526 mmHg. I started with three identical glass containers each holding 100ml about 35 fl. M is the molality.
A solution boils at a slightly higher temperature than the pure solvent. How to use freezing point in a sentence. The change in the boiling point is calculated from.
When the opposite happens and a liquid turns into a solid it is called freezing. When a liquid becomes a gas it is called boiling or vaporization. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators.
Thus as solutes or solids are applied to liquids the freezing point drops and the boiling point rises. Click to see full answer. A similar property of solutions is boiling point elevation.
The normal boiling point of water is 100 o C because this is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of water is 760 mmHg or 1 atm. Note that ceCaCl_2 is substantially more effective at lowering the freezing point of water because its solutions contain three ions per formula unit. A freezing point is the temperature at which a liquid transitions to a solid.
The red line shows the atmospheric pressure of the selected planet. In Celsius the boiling and freezing points of water are 100 and 0 respectively. Therefore the boiling point elevation would be 2oC.
In Fahrenheit those would be 212 and 32. T K f m. Because the freezing point of pure water is 0C the actual freezing points of the solutions are 22C and 30C respectively.
I knew that the water would not turn from liquid to ice all at once and I puzzled over when to consider the water. Asked May 7 2018 in Physics by paayal 147k points The efficiency of an ideal heat engine working between the freezing point and boiling point of water is -. The freezing point depression is the amount that the freezing temperature decreases.
For example an altitude change of only 28 cm 11 in causes the boiling point. About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. He came up with this temperature scale based on the three fixed temperature points of the human body freezing water and a mixture of ice salt ammonium chloride and water.
The Fahrenheit scale defines the freezing point of water as 32F and the boiling point as 212F. The blue line shows the vapor pressure of water as a function of temperature. Under normal conditions when the pressure of the atmosphere is approximately 760 mmHg water boils at 100 o C.
The bag of the salt became colder so the mixture froze faster. The boiling point is the temperature at which the vapor pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure. The melting point for water is 0 degrees C 32 degrees F.
For example the boiling point of pure water at 10atm is 100oC while the boiling point of a 2 saltwater solution is about 102oC. Freezing point definition is - the temperature at which a liquid solidifies. Oz of filtered water.
The freezing point of water is the same as its a. I put all these into my freezer which had an air temperature of 0F 18C. In fact ceCaCl_2 is the salt usually sold for home use and it is also often.
Where T is the freezing point. The Celsius scale sets the freezing point and boiling point of water at 0C and 100C respectively.
Density And Specific Gravity Relation
Difference Between Density and Specific Gravity. Newtons universal law of gravitation states that the force of gravity acting between two objects remember the forces of gravity that.
 What Is Specific Gravity Definition Formula Calculation Examples General Class 2021 Video Study Com
What Is Specific Gravity Definition Formula Calculation Examples General Class 2021 Video Study Com
Density is the material per unit volume.

Density and specific gravity relation. Specific Gravity of gases is normally calculated with reference to air - and defined as the ratio of the density of the gas to the density of the air - at a specified temperature and pressure. Well yes but actually no. Volume of soil solid in a given soil mass.
Define density specific weight and specific gravity. The Specific Gravity can be calculated as. 1146 specific gravity Density of a substance g m L Density of the water at the same temperature g m L If a substances relative density is less than one then it is less dense than water and similarly if greater than 1 then it is denser than water.
There is a noticeable difference between density and specific gravity even though both are used to represent mass and are used to compare different substances. Even if specific gravity and density both are used to represent mass these quantities are quite different from one another. If the relative density is exactly 1 then the densities are equal.
Because the density of water is very nearly 1 gcm 3 the density of any substance in gcm 3 is nearly the same numerically as its specific gravity relative to water. Both density and specific gravity and their relationship are explained. When the reference substance is water in case of solids or liquids and hydrogen in case of gases the relative density is referred to as specific gravity.
Weight of soil solid in a given soil mass. Volume of water present in the given soil mass. Specific gravity which is also called as relative density is a measure of density with respect to a density of pure water.
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. Specific gravity is an expression of density in relation to the density of a standard or reference usually water. In this article we will make a formula or equation or relation between void ratio e water content w degree of saturation and specific gravity G.
Write the relation between density and specific weight. Is there a relationship between density and gravity. The main difference between density and specific gravity is that density is the mass per unit volume of the substance whereas specific gravity is a ratio comparing the density of one substance to the density of another reference substance.
Density and specific gravity are both used to describe mass andcanbe used to comparesubstances. A plate at 05 mm distance from another fixed plate moves at 025 ms. Specific gravity is in direct relationship with density.
The key difference between density and specific gravity is that density is an absolute value while specific gravity is a. What I mean is not really. Relative Density RD Density of a substance Density of a reference substance.
INTRODUCTIONThe Density is the mass per unit volume of a material. It is the ratio of an objects density and its contact substance. Specific gravity is the ratio of the density of a substance to the density of a reference substance.
For example if you want to place an object in water the specific gravity would tell you if it would float or not. Both these concepts hold almost the same idea. Being a ratio the relative density has no unit.
One gallon of mercury has a mass of 512 kg. The ratio of mass per unit volume is known as the density of a liquid. On the other hand specific gravity refers to the relative density of a fluid with respect to another liquid usually water.
Weight of water. Specific gravity is a measure of the ratio of mass of a given volume of material at 23C to the same volume of deionized waterThere are two basic test procedures that we performed with the help displacement methodMethod A and Method B. SG ρ gas ρ air 3 where SG specific gravity of gas ρ gas density of gas kgm 3.
In the English system of units the density of water is about 624 lbft 3 so the near equality between specific gravity and density is not preserved in this system. Also density is expressed in units weight relative to size while specific gravity is a pure number or dimensionless. These concepts are very useful in the food industry rubber industry and whole of the material science.
On the other hand density is expressed in terms of kgm3 SI. Relative density and specific gravity are two concepts used in comparing densities of solids liquids and gas. Density is the property of matter represented by a ratio of mass to a unit volume of matter.
Example Of Natural Active Immunity
Examples of natural immunity are the lysozyme found in tears saliva and other body secretion acidic pH of the gastrointestinal and vaginal tracts and interferon produced by body cells to protect against viruses. Natural Active Immunity.
 Difference Between Active Immunity And Passive Immunity Explained
Difference Between Active Immunity And Passive Immunity Explained
Wild infection for example with hepatitis A virus HAV and subsequent recovery gives rise to a natural active immune response usually leading to lifelong protection.
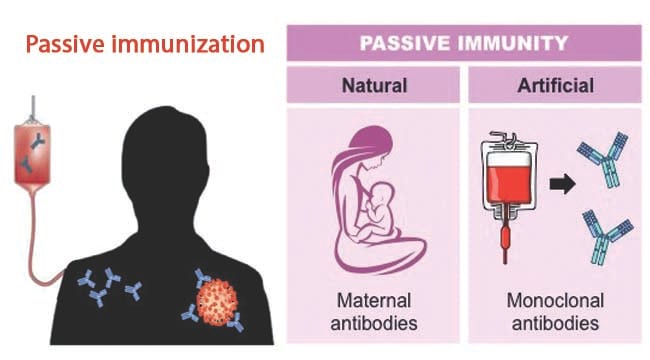
Example of natural active immunity. Active immunity is immunity that develops as a result of natural or deliberate exposure to an antigen. Vaccinations stimulate the immune system with an antigen. Immunization of chickenpox hepatitis flu and polio are some examples of active immunity.
Also known as natural resistance. This type of immunity is natural because deliberate exposure does not induce it. To artificially immunize an individual a weakened or killed version of the same antibody is used against which the immunity is sought.
And The IgA and IgG found in human colostrum and milk. An allergic reaction is an extreme response to an antigen resulting from active immunity. In a similar manner administration of two doses of hepatitis A vaccine generates an acquired active immune response leading to long-lasting possibly lifelong protection.
The placental transfer of IgG from mother to fetus during pregnancy that generally lasts 4 to 6 months after birth. Exposure to the disease organism can occur through infection with the actual disease resulting in natural immunity or introduction of a killed or weakened form of the disease organism through vaccination vaccine-induced immunity. The IgA and IgG found in human colostrum and milk of babies who are nursed.
In addition to the IgA and IgG. Naturally acquired active immunity occurs when a person is exposed to a live pathogen and develops a primary immune response which leads to immunological memory. For example a by-product of the enzymatic activity of the complement system acts as a chemotactic factor attracting T lymphocytes and macrophages to the invasion site.
Acquired immunity makes your immune system stronger. In another example although T lymphocytes are not required for the production of antibody there is optimal antibody production after interaction between T and B lymphocytes. Natural immunity is a general and non-specific resistance to infection possessed by all healthy individuals.
The immune system creates its defense against the antibody by the eventual production of antibodies. Natural immunity The ability to resist infection that does not depend on prior experience of the invading organism and the resultant production of antibodies or amendment or selection of LYMPHOCYTES. Active Immunity - antibodies that develop in a persons own immune system after the body is exposed to an antigen through a disease or when you get an immunization ie.
There are two examples of passive naturally acquired immunity. The body responds by making its own antibodies. A baby receiving antibodies from her mothers breast milk and injection of antisera are examples of passive immunity.
This ensures that when the individual comes in natural contact with this antigen later the immune. These antibodies generally last 4 to 6 months. Learn Examples On Natural Acquired Active Immunity Meaning Concepts Formulas Through Study Material Notes Embibe Com Micro Ch16 Preparation Cell Mediated Humoral Response Flashcards Quizlet Give An Example Of Artificially Active Immunity And Artificially Passive Immunity Biology Mineral Nutrition 12602809 Meritnation Com Artificially Acquired Active Immunity Example.
A vaccination is an example of active immunity. Natural active immunity occurs when an individual comes in natural contact with an antibody. Active immunity results when exposure to a disease organism triggers the immune system to produce antibodies to that disease.
The immune system then produces B and T cells that quicken and strengthen the bodys response to repeated infection. Either way if an immune person comes into contact with that disease in the future their immune. Active naturally acquired immunity refers to the natural exposure to an infectious agent or other antigen by the body.
Vaccines for example expose your immune system to small amounts of pathogens that wont make you sick. The placental transfer of IgG from mother to fetus during pregnancy. Examples of Active Immunity An example of natural activity immunity is fighting off a cold.
An example of artificial active immunity is building up a resistance to a disease due to immunization. The phenomenon of natural immunity can be illustrated equally well with examples from the respiratory intestinal or genital tracts where large surface areas are exposed to potentially infective agents and yet infection does not occur. There are two examples of passive naturally acquired immunity.
Immunity that develops after exposure to a disease-causing infectious microorganism or other foreign substance such as following infection or vaccination. If an organism causes local infection or gains entry into the bloodstream a complicated series of events ensues.